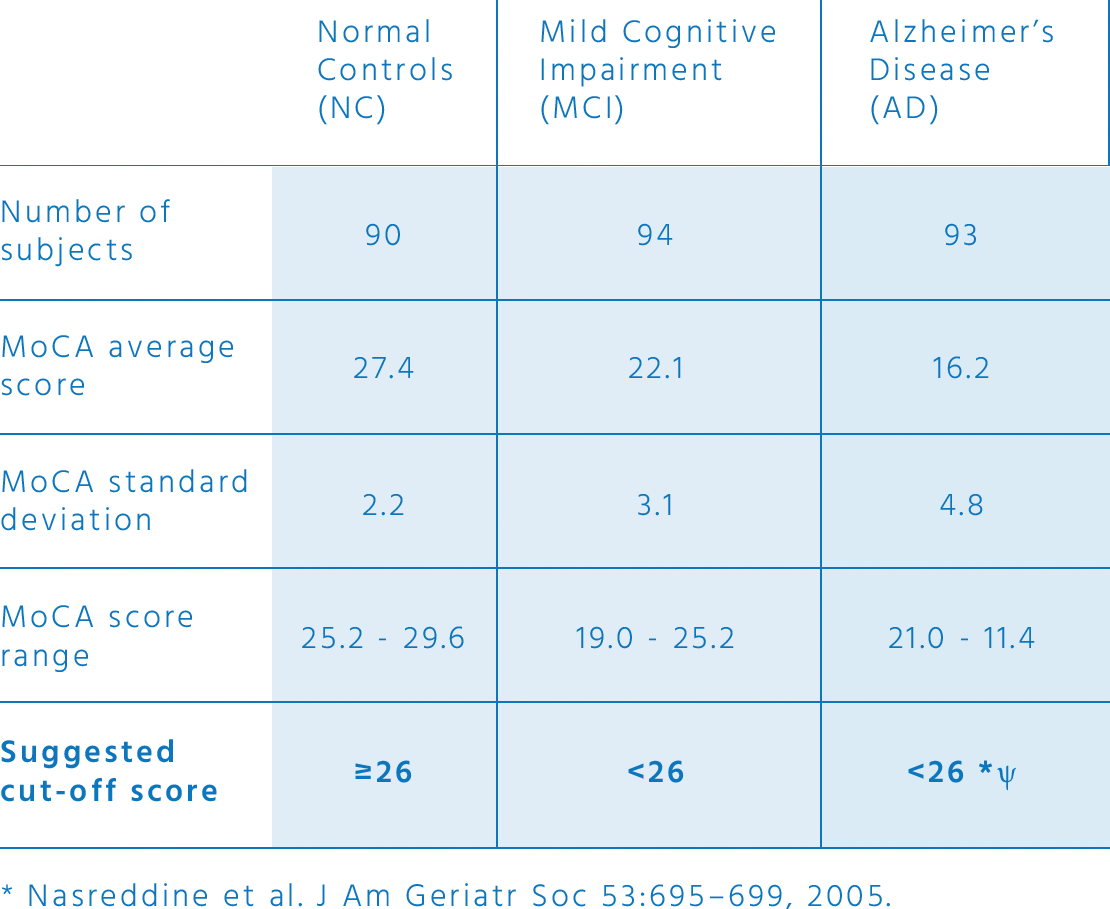
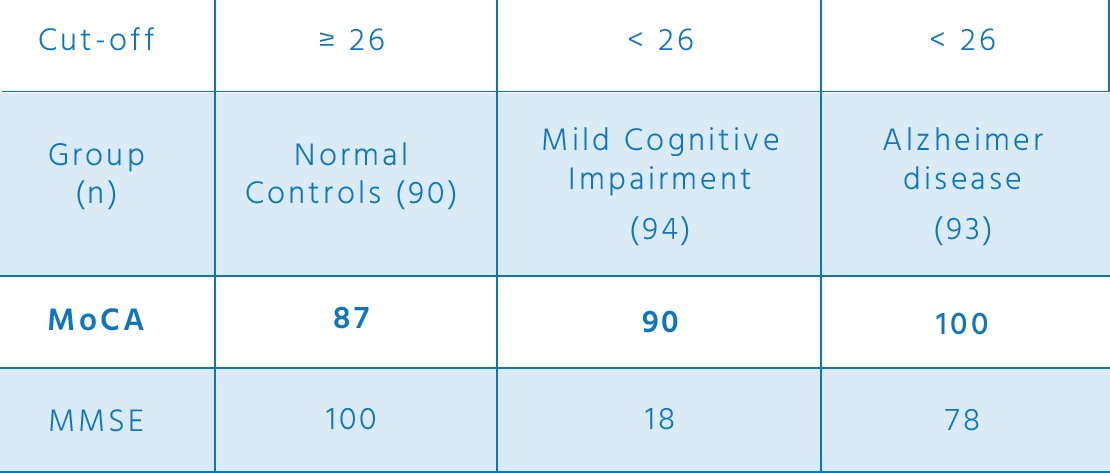
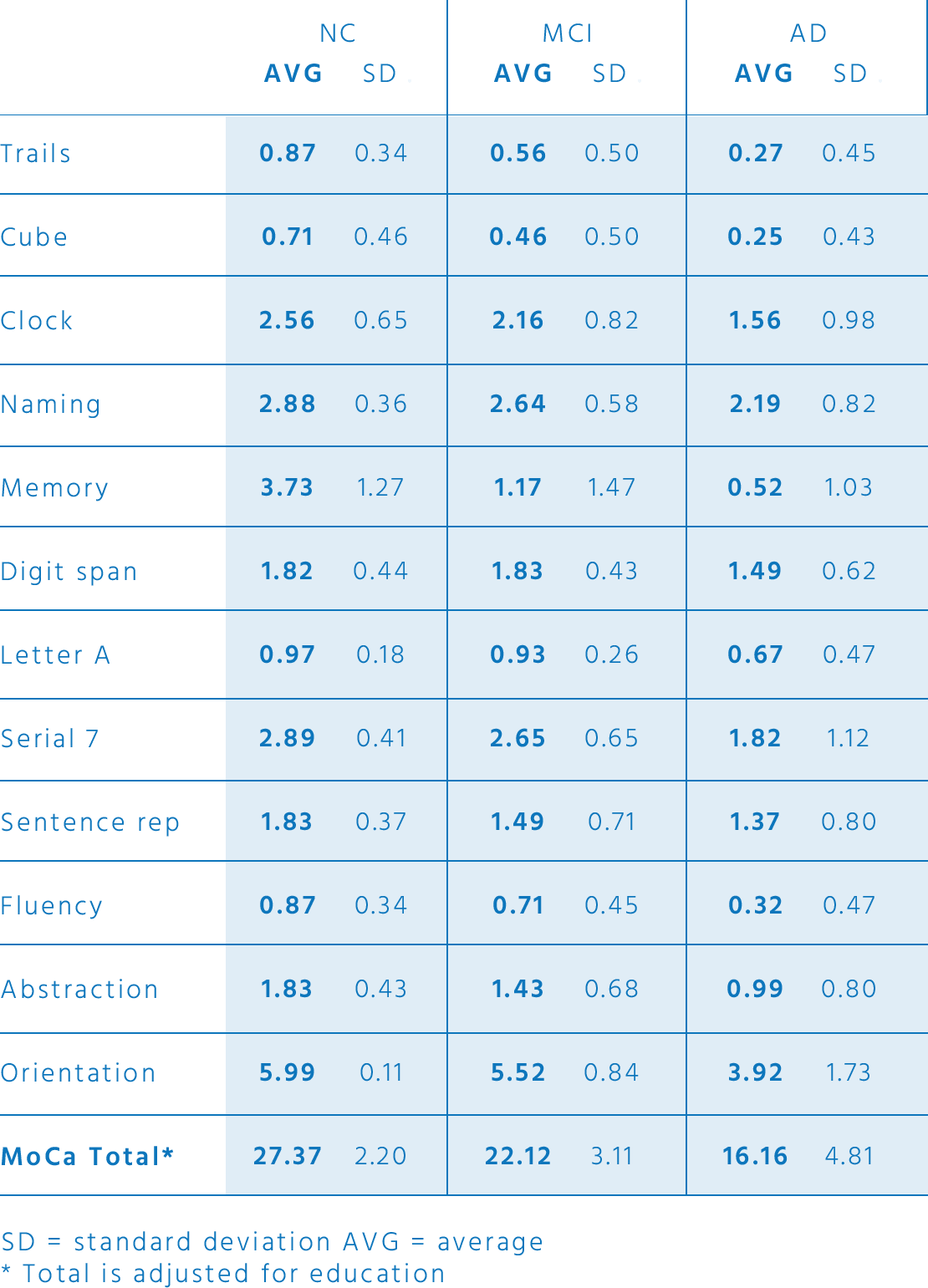
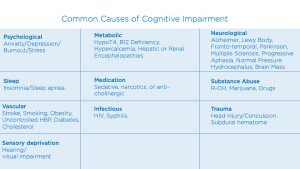
Consult the latest education and age based norms of the test, average scores for normal, mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Test retest and item by item performance. Sensitivity, specificity and cut-off scores of the MoCA to detect mild cognitive impairment or Alzheimer’s disease and distinguish it from normal aging.
For more information on clinical data, consult the MoCA validation study: Nasreddine, Z. S., Phillips, N. A., Bédirian, V., Charbonneau, S., Whitehead, V., Collin, I., … & Chertkow, H. (2005). The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: a brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 53(4), 695-699.
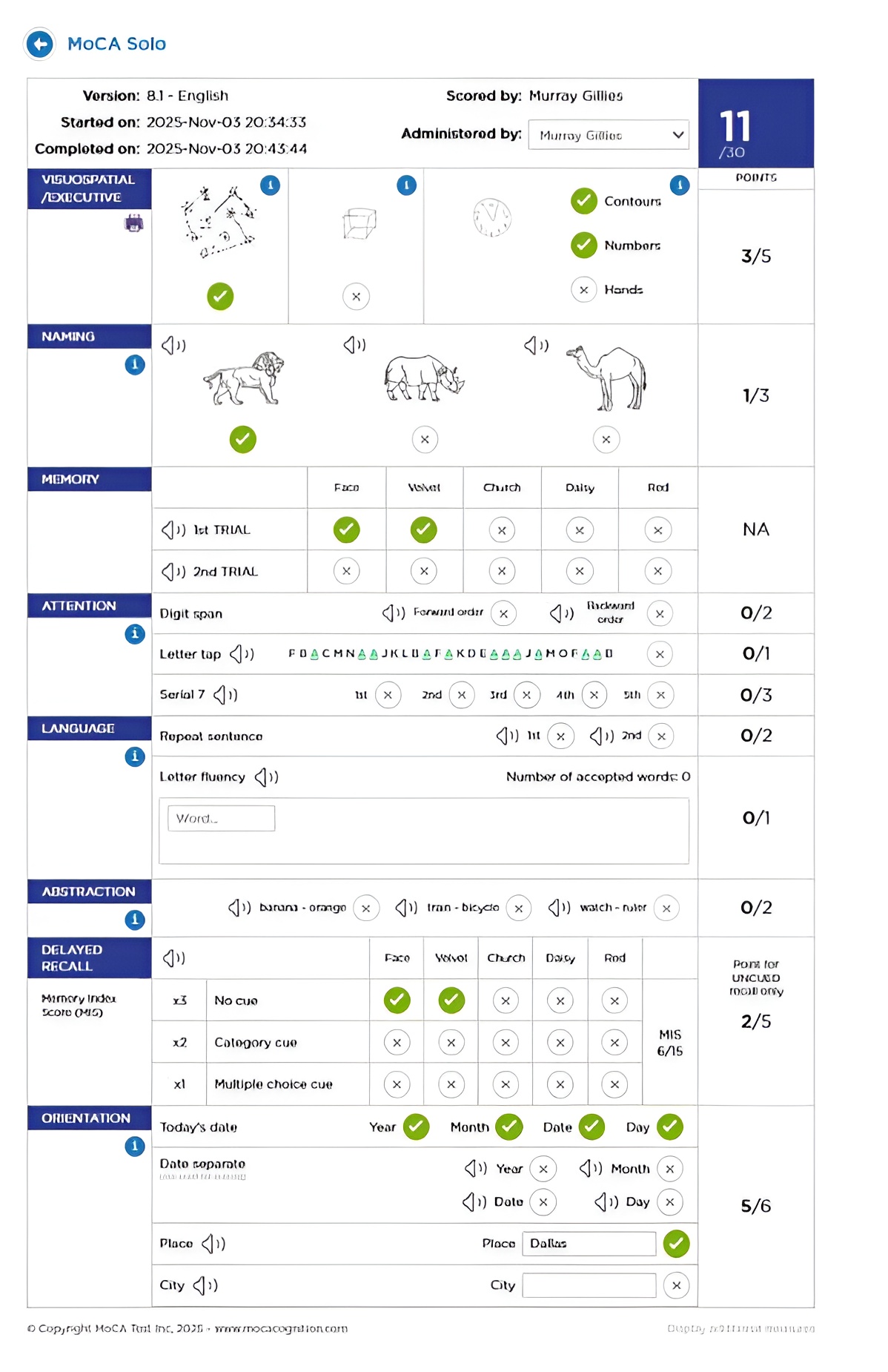
Ensuring the MoCA Solo User
Interface is clear for people with
Cognitive Impairment
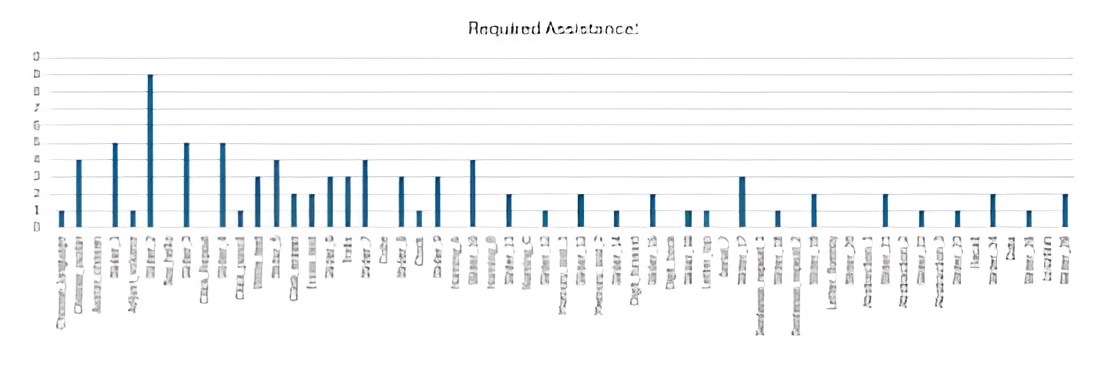
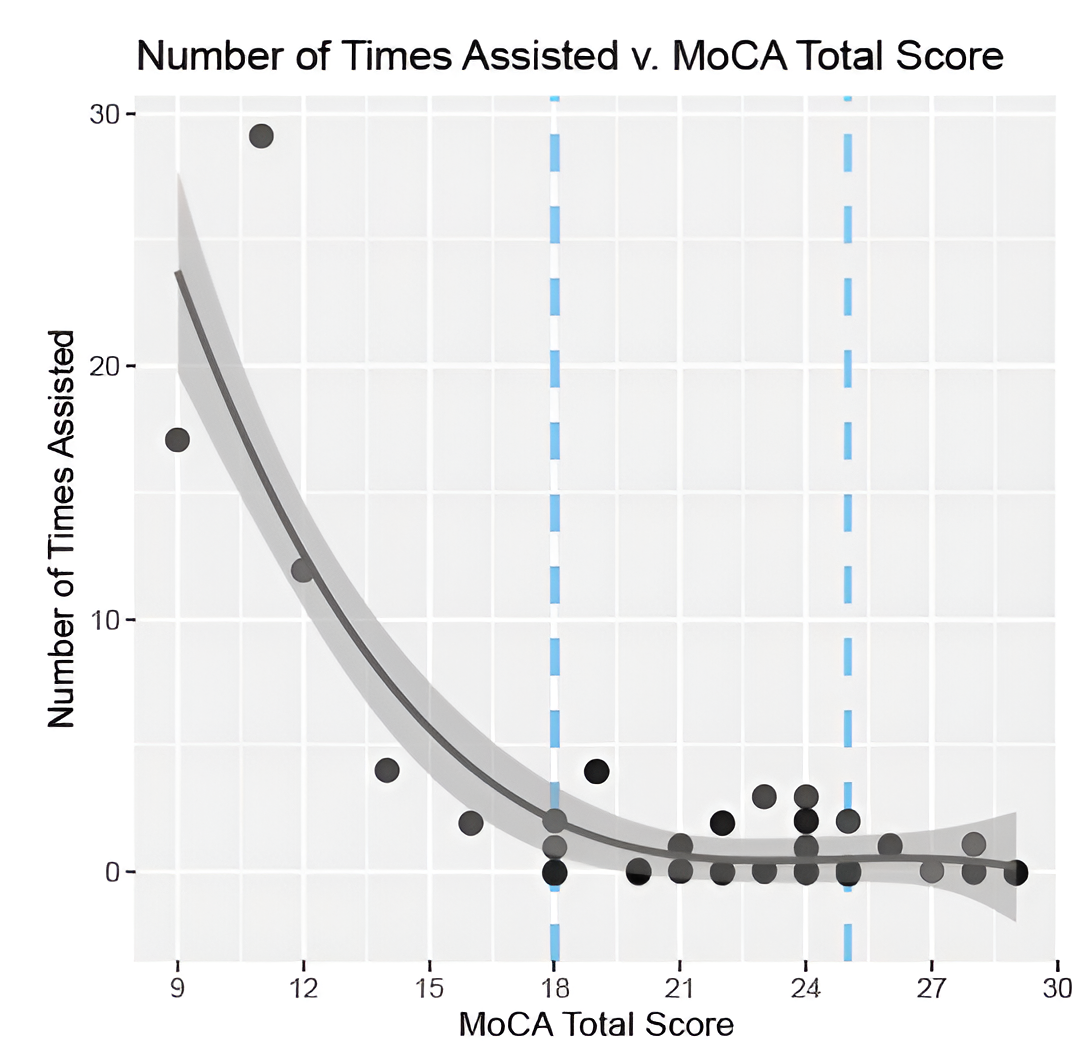
UX steps vs numbers of times assistance needed
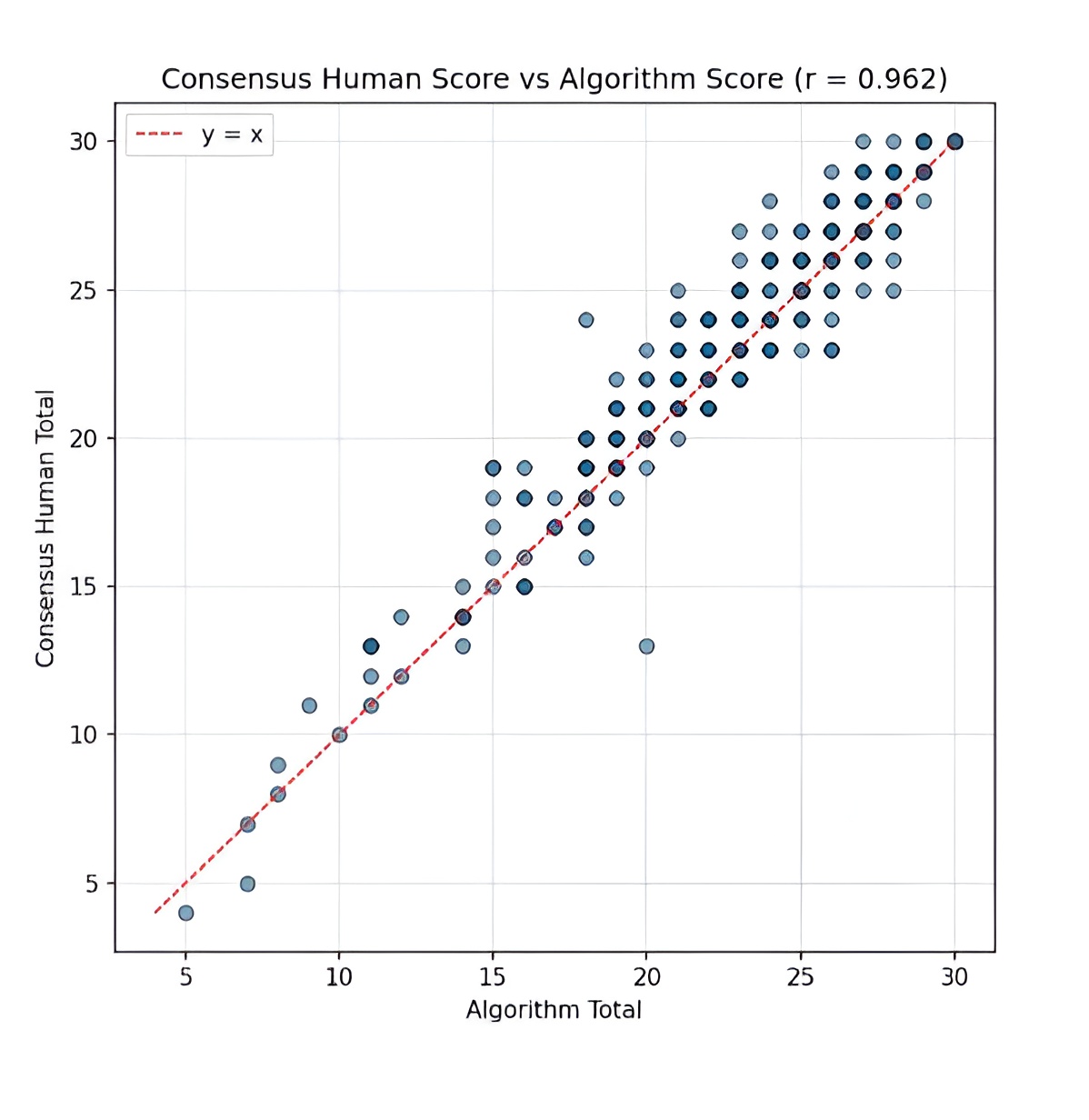
MoCA Solo comparison of AI scoring vs human
The figure above shows the total MoCA
score as scored by 3 humans, forming
consensus, compared to the ai score for a
group of 300 individuals.
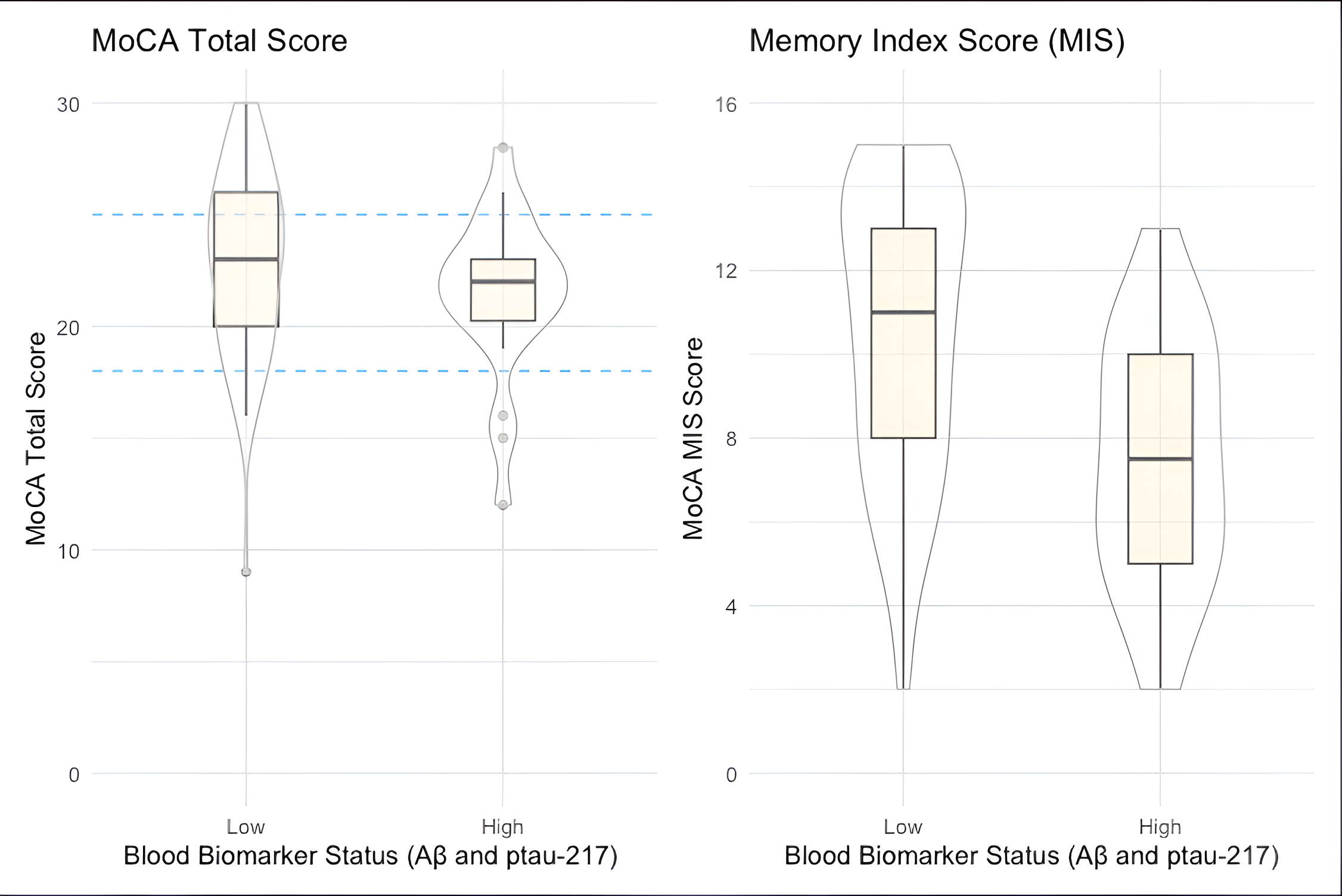
The MIS as measured with the MoCA Solo
shows strong correlation to BBM positivity
Submitted to AAIC2026:
“Plasma Biomarkers are Associated
with Lower Memory Index Scores
and Recent Cognitive Decline” W.
Huijbers et al
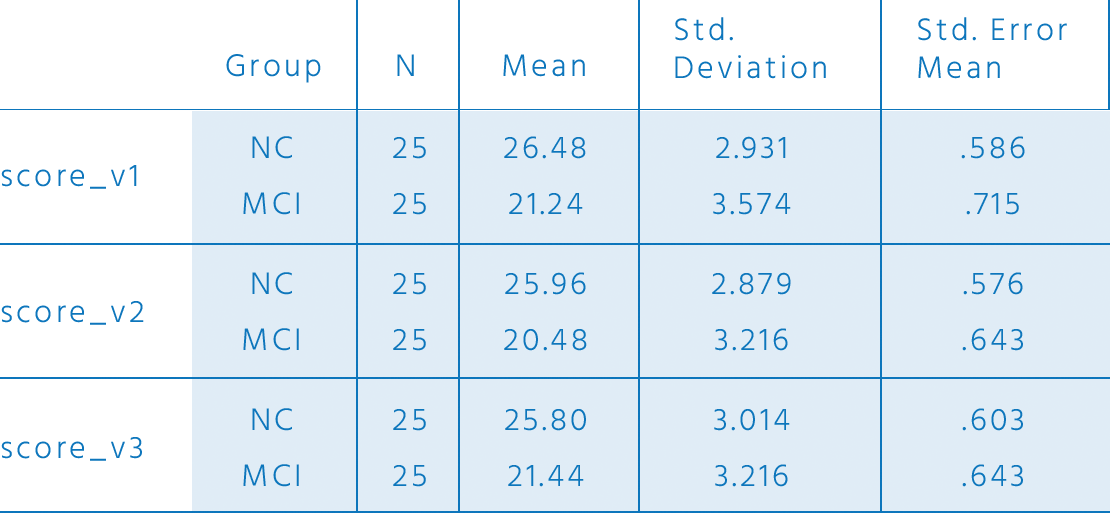
Moca items
average scores
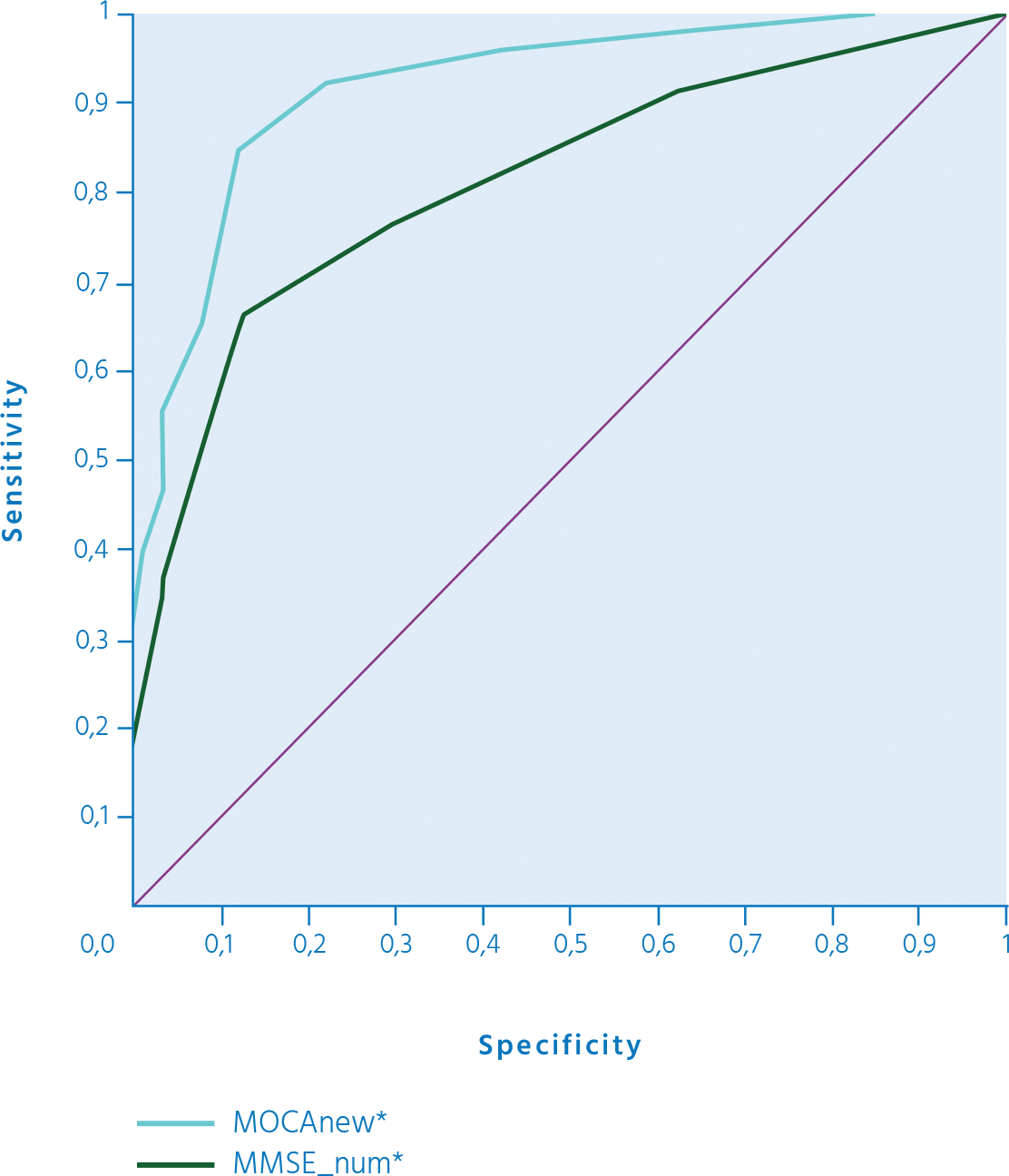
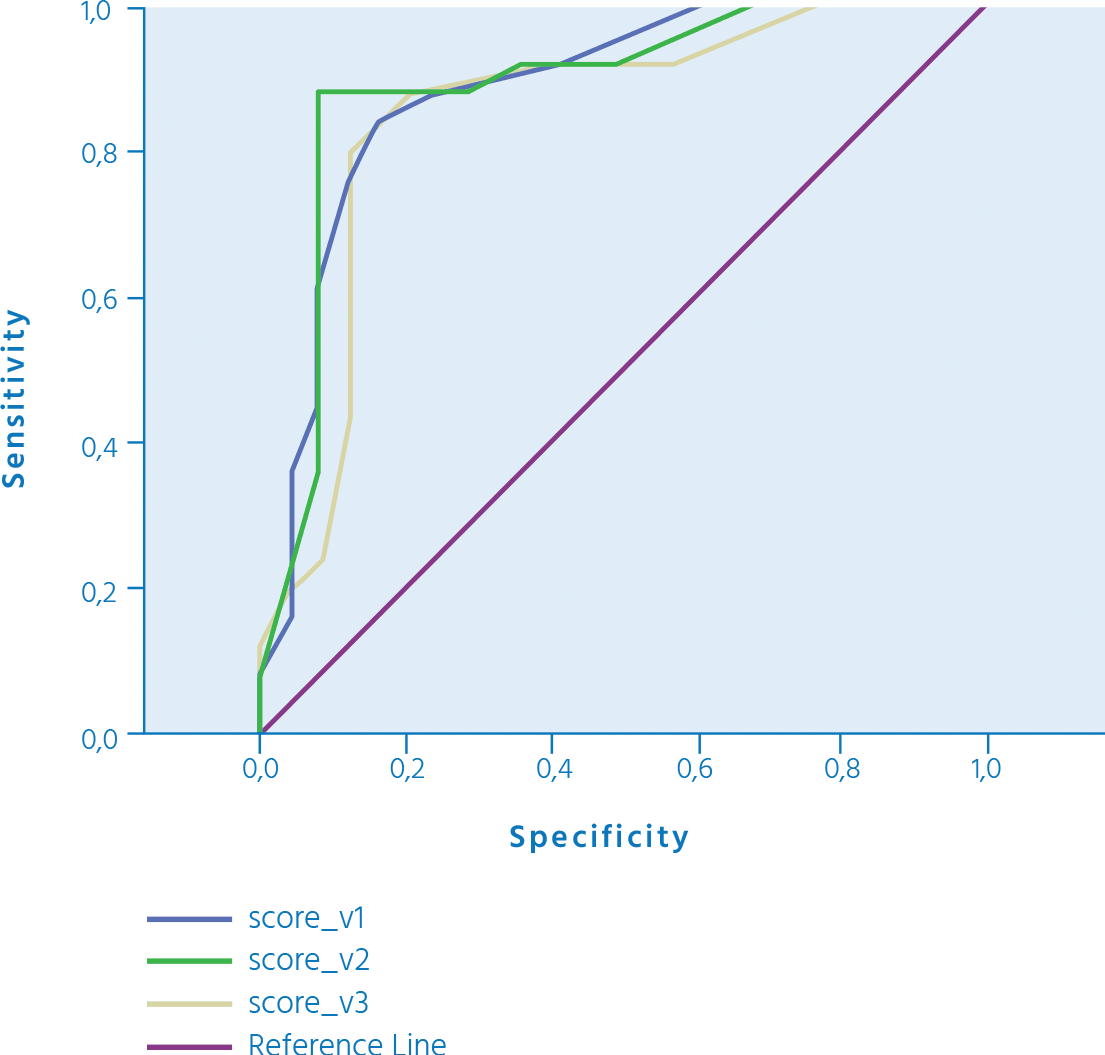
ROC CURVE FOR
MOCA and mmse
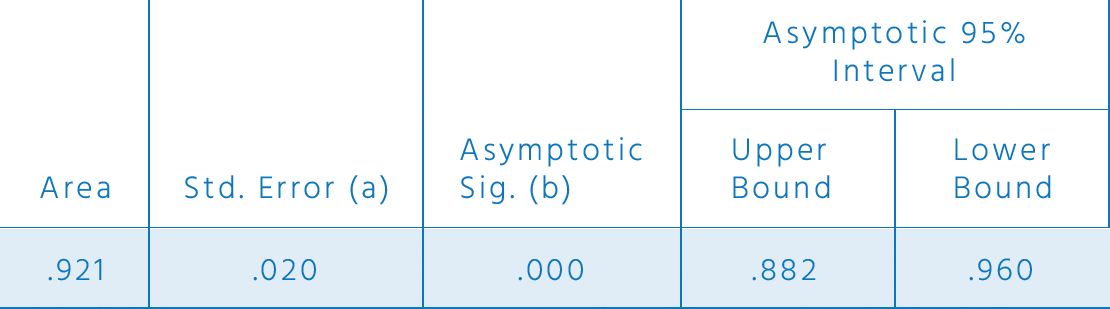
Area Under
the Curve
Test Result Variable(s): MoCA
Lower BoundUpper BoundLower Bound
The test result variable(s): MOCA new has at least one tie between the positive actual state group and the negative actual state group. Statistics may be biased.
(a) Under the nonparametric assumption.
(b) Null hypothesis: true area = 0.5
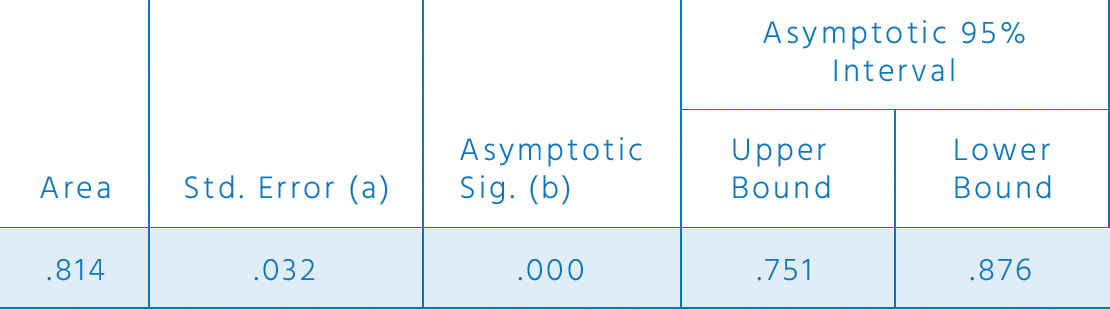
Area Under
the Curve
Test Result Variable(s): MMSE
Lower BoundUpper BoundLower Bound
The test result variable(s): MMSE_num has at least one tie between the positive actual state group and the negative actual state group. Statistics may be biased.
(a) Under the nonparametric assumption.
(b) Null hypothesis: true area = 0.5